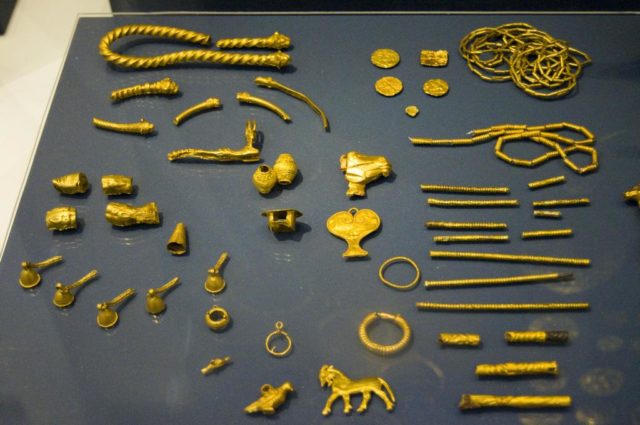
An incredible treasure discovered near the Oxus River is one of the most precious collections of ancient Persian artifacts. Only 180 pieces of jewelry, plaques, and statuettes, and about 200 coins have survived the years, but the original cache was much bigger. Comprised of stunning gold and silver artifacts, the treasure is an impressive example of ancient wealth. The elaborately decorated metalwork also shows how skillful artists were in Persia during the 2nd or 3rd centuries BC.
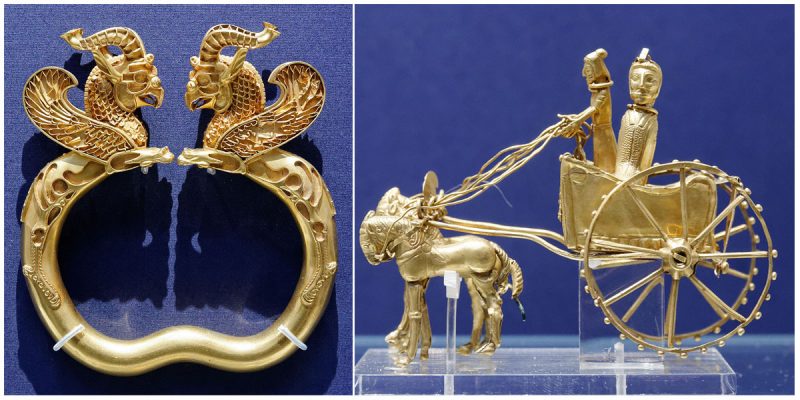

Dividing the Achaemenid Treasure
The impressive Oxus Treasure was discovered at the end of the 19th century. However, the time delay between excavations and the moment when the metal artifacts were cataloged and exhibited created problems for maintaining the precious pieces as one complete collection. Many of the priceless artifacts have been lost forever. Some Oxus artifacts seem to be located in different museum collections, but due to the lack of documentation it is impossible to conclude their origins.
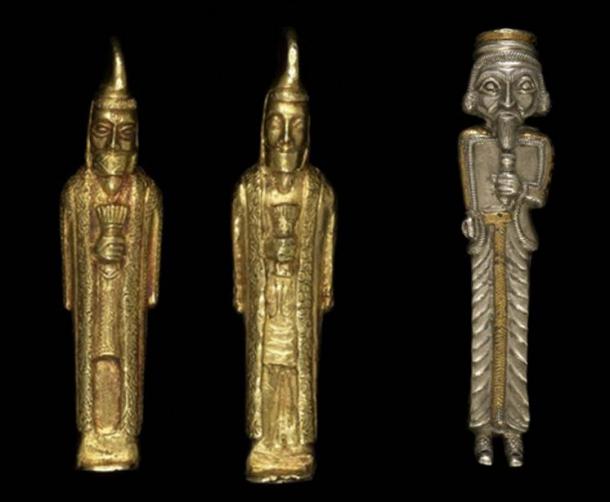

Gold statuettes of bearded men (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) and cast and chased silver statuette of another bearded man. (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) All from the Oxus Treasure.
The Oxus Treasure by John Curtis (published by the British Museum) details one occasion on which the treasure was divided. Curtis writes:
“A large part of the treasure was nearly lost in 1880 and only recovered by chance in extraordinary, even bizarre circumstances. According to O.M. Dalton, whose 1905 catalog of the Oxus Treasure remains the basic publication, in May of that year three merchants from Bokhara, who presumably bought the treasure from local villagers, were travelling with it from Kabul to Peshawar. East of Kabul they were attacked by local tribesmen, who seized them and the Treasure. However, their servant was able to escape and raised the alarm in the camp of Captain E C. Burton, a political officer in Afghanistan. Burton set off with two orderlies and came across the robbers in a cave shortly before midnight. They were in the process of dividing up their spoil and were already quarrelling over it. Four were lying wounded. We are told that “a parley ensued”, as a result of which much of the Treasure was given up to Burton. The next day he threatened to lead a force against the robbers, which persuaded them to bring in another large part of the Treasure. In this way about three quarters was restored to the merchants and, as a token of their gratitude, they allowed Burton to purchase the large gold armlet subsequently acquired by the Victoria and Albert Museum.”
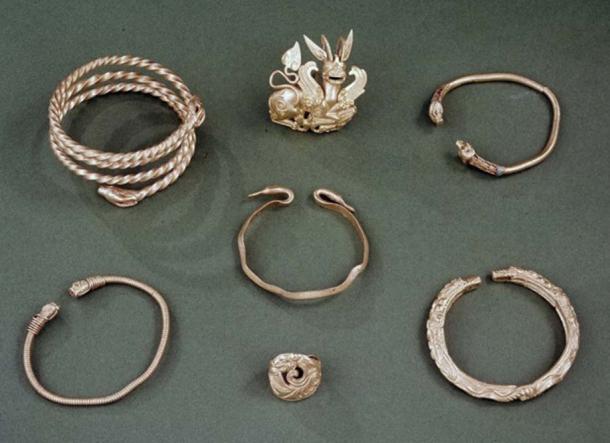

Several pieces of jewelry from the Oxus Treasure. (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Beautifully Decorated Metalwork


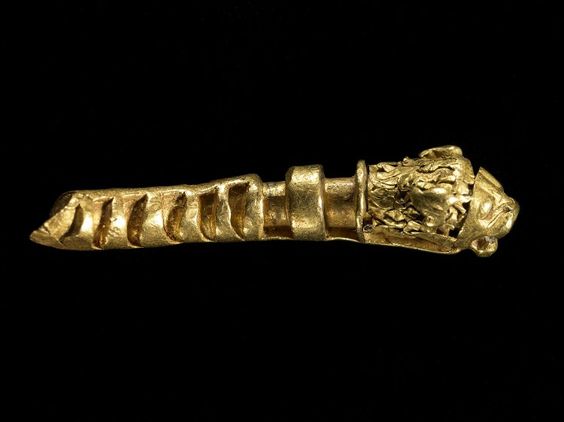
A gold armlet with griffin heads from the Oxus Treasure. (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
The valuable treasure also includes interesting and detailed sculptures. There are small figurines and a few larger objects. Some of the figures representing males may depict priests or other people worshipping ancient deities. The largest of the known figurines shows a nude young man made of sliver. This rare artifact is more characteristic to the ancient Greek than Persian style.
Outside cultural influence may also be seen in the sculpture depicting the face of the Egyptian god Bes – a dwarf who was a protective deity; and one of the golden plaques formed in the shape of a lion or griffin which is believed to be Scythian, based on the characteristic way its legs were made.



The silver statue of the young man. (Public Domain)
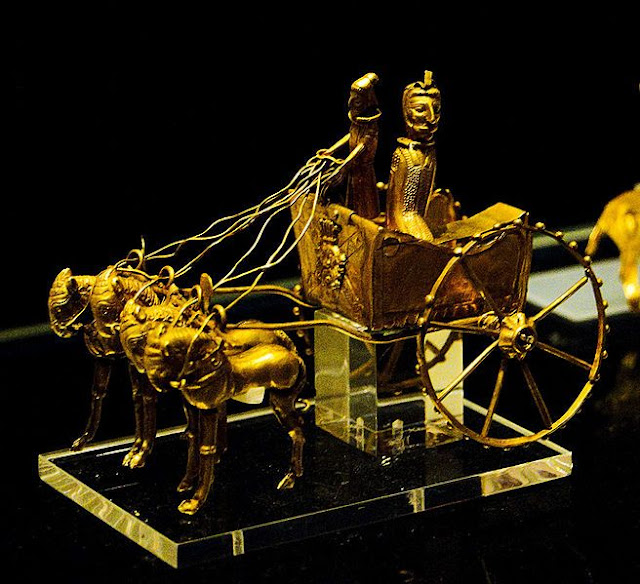
Apart from this, two gold models of chariots are also very eye-catching. One of them is incomplete, but the second is in a perfect state of preservation. There were also some figures of horses and riders that almost surely belonged to this set of figurines.
Vessels, Coins, and Other Precious Treasures
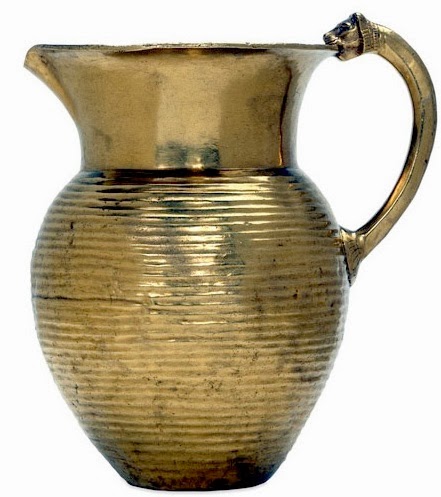
Several of the vessels discovered near the Oxus River are now located in London. This group of artifacts includes a golden jug and bowls. These items were also decorated with motifs of real and mythical animals. One of the most interesting vessels is a hollow gold fish, which depicts a species of carp that is only found in the Oxus River.


The hollow gold fish vessel. (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
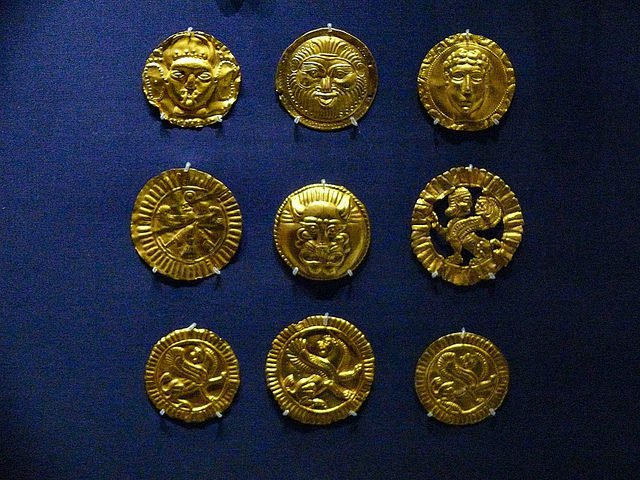
51 thin gold plaques are decorated with devotees making offerings to their deities. The plaques are shaped like rectangles. The smallest of these offering plaques is just 2 cm (0.79 inches) tall, while the biggest is ten times larger.
Finally, the coins discovered in the Oxus Treasure depicted Antiochus the Great (223-187 BC), Euthydemus I of Bactria (235 – 200 BC), and Alexander the Great. Researchers unearthed at least 521 coins. Together, these artifacts helped them date the magnificent treasure to the beginning of the 2nd century AD.
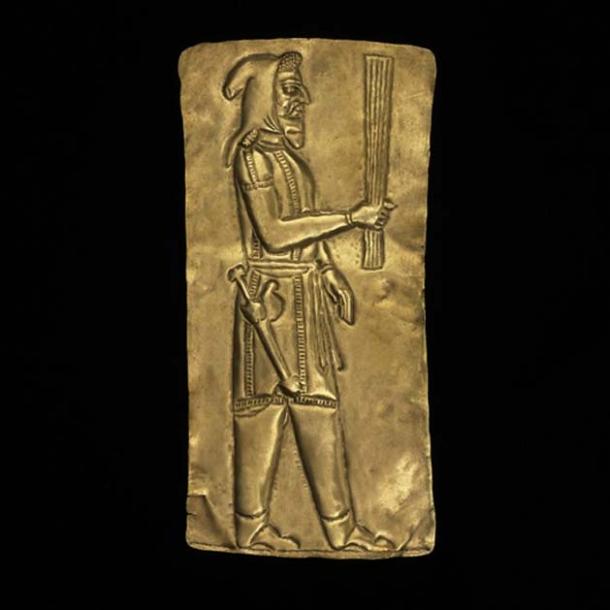


One of the votive plaques. (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Unanswered Questions on a Scattered Treasure
Unfortunately, further details about the treasure were lost during excavations and over the decades following its discovery. Two of the biggest problems are identifying the original owner and finding out why it was buried near the Oxus River.
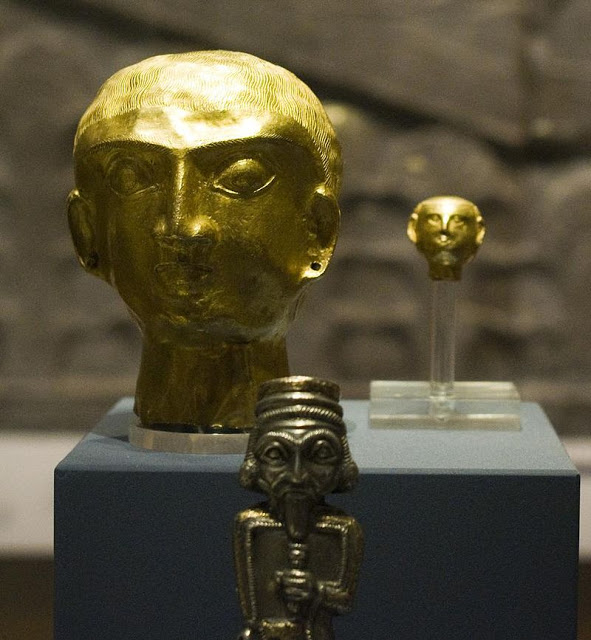


Hollow gold heads of beardless men made from a single piece of hammered sheet, Oxus Treasure. (British Museum/CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Now, most of the known pieces of the Oxus Treasure are located in London. Some of the artifacts are believed to be in St Petersburg, but this is uncertain. Although the cache was taken to Europe and is not in its homeland, the destruction of many valued aspects of Persian heritage means that it is still one of the greatest treasures from the ancient Achaemenid Empire.





